Leave a message
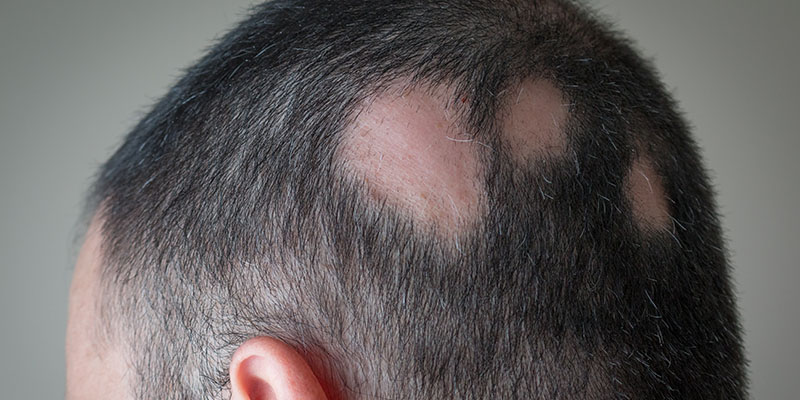
Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune skin resulting in hair loss on the scalp, face and sometimes other body parts that have hair growth. It is an autoimmune disorder in which the patient’s immune system starts attacking their hair follicles.
It presents in the majority of cases as localised patches of non-scarring hair loss.
It is in the majority of cases; that alopecia presents as one or more well-defined patches of hair loss. It can be diffused, affecting most of the scalp. However, at times patients’ lose hair on their entire scalp or body, which is referred to as alopecia totalis.
Alopecia areata can also affect the fingernails and toenails. Sometimes, these changes are the first sign of the condition. Several small changes can occur to nails:
Unfortunately, there is no cure for alopecia areata. However, some treatments can encourage hair regrowth or methods that can slow down the effects of alopecia.
The most common form of alopecia areata treatment is corticosteroids, powerful anti-inflammatory drugs that can suppress the immune system. A dermatologist most commonly administers these through local injections, topical ointment application, or orally.